The rite of burial dates back 100,000 years. In many cultures, human bodies are buried in soil which can be seen as an attempt to lessen the pain of losing a loved one by interring a body away from plain view and marking the gravesite with a headstone. However, a body may be buried above ground in a mausoleum, either public or private. In a traditional burial, the deceased is housed in a casket usually made of wood or metal and the body is embalmed for preservation between the time of death and burial. A burial vault is a lined and sealed outer receptacle that houses and protects the casket.
In modern times, the custom of burying dead people below ground in a casket or coffin, with a stone marker to indicate the burial place, is used in most cultures. Also, a body may be buried above ground in a mausoleum, either public or private. However, in a traditional burial, the deceased is housed in a casket usually made of wood or metal and the body is embalmed for preservation between death and burial. A burial vault is a lined and sealed outer receptacle that houses and protects the casket.
The cremated remains of a person may also be buried below ground in an urn containing cremated remains. Burials may take place on land or at sea. Burial at sea is the disposal of human remains in the ocean, normally from a ship or boat. It is regularly performed by navies, and also takes place by private citizens in many countries. The ceremony may include burial in a casket, burial in an urn, or scattering of the cremated remains over the water.
Recently, revolutionary methods of burial are surfacing with ecology in mind. They are known as “green burials”. Simply wrapping the body in a shroud without other protection is widely accepted and permits the body to decompose into the earth. Other methods support the growing of a tree by using the decomposing body or ashes for fertilizer. To some, leaving behind a tree definitely seems like a better option than leaving behind a tombstone.
To Learn More:
www.navy.mil/navydata/questions/burial.htm
www.funeralplan.com/funeralplan/cremation/sea.htm
http://bigthink.com/design-for-good/this-awesome-urn-will-turn-you-into-a-tree-after-you-die
www.boredpanda.com/biodegradable-burial–pod-memory-forest-capsula-mundi/

Even though the words are used synonymously, there is a difference between a casket and a coffin. Caskets are rectangular in shape and are constructed of high quality materials
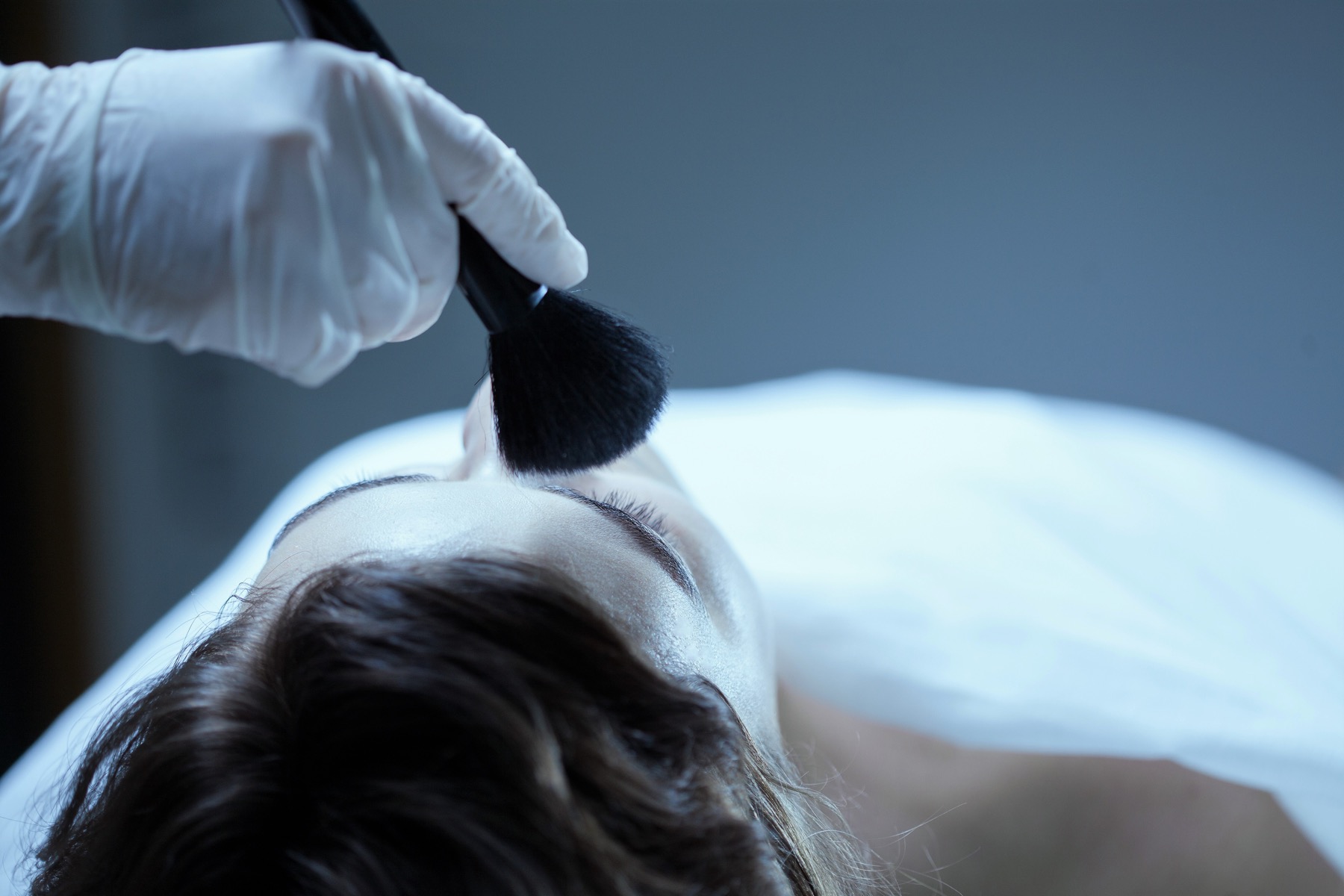
The term Desairology is one we rarely hear. Even in the funeral industry, where the term was coined, most funeral professionals have never heard the term.
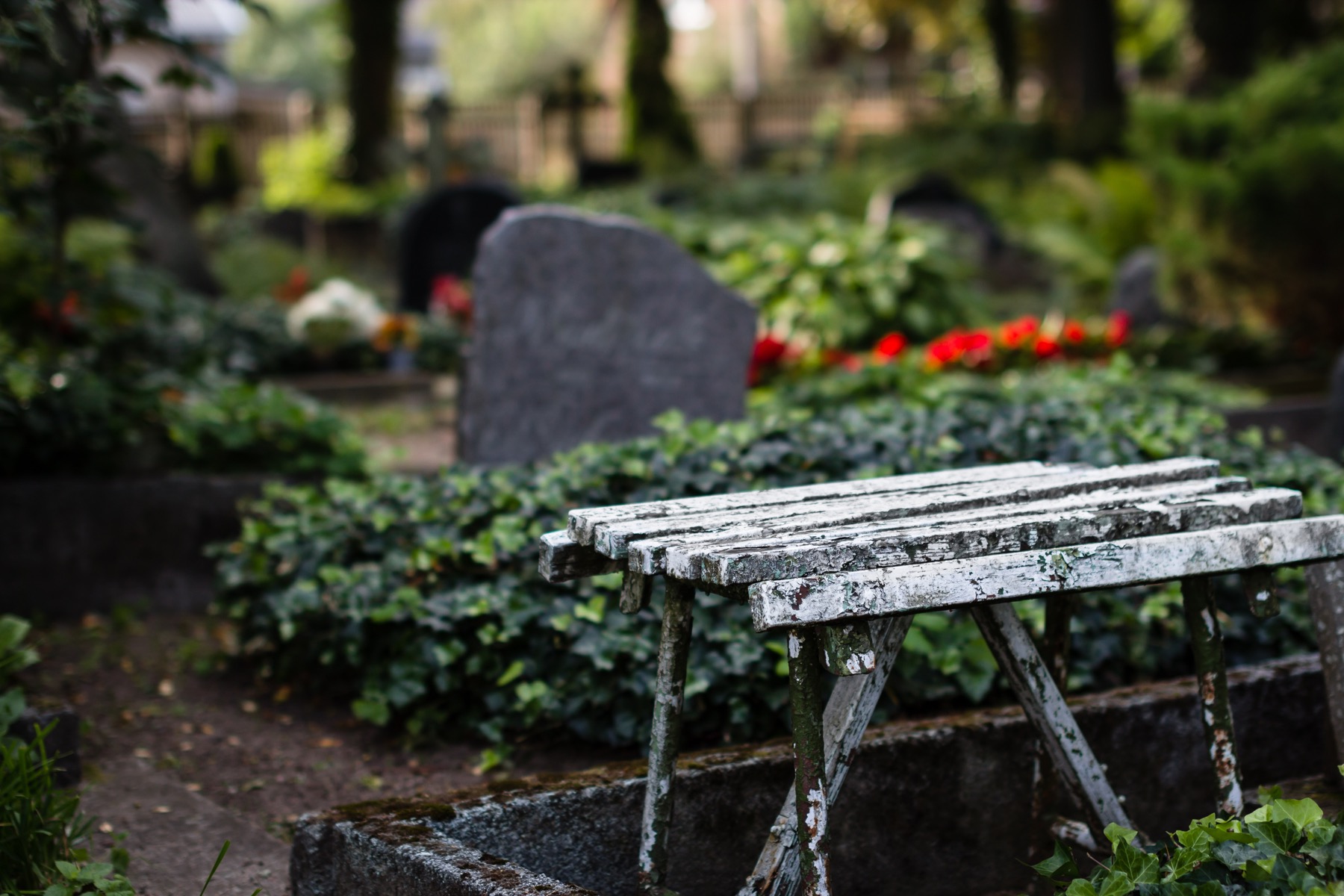

Cemeteries in the U.S. range from national, military, private, city, religious and green cemeteries, each with varying degrees of purpose and motivations.

The rite of burial dates back 100,000 years. In many cultures, human bodies are buried in soil which can be seen as an attempt to lessen the pain of losing a loved one by interring a body away from plain view.
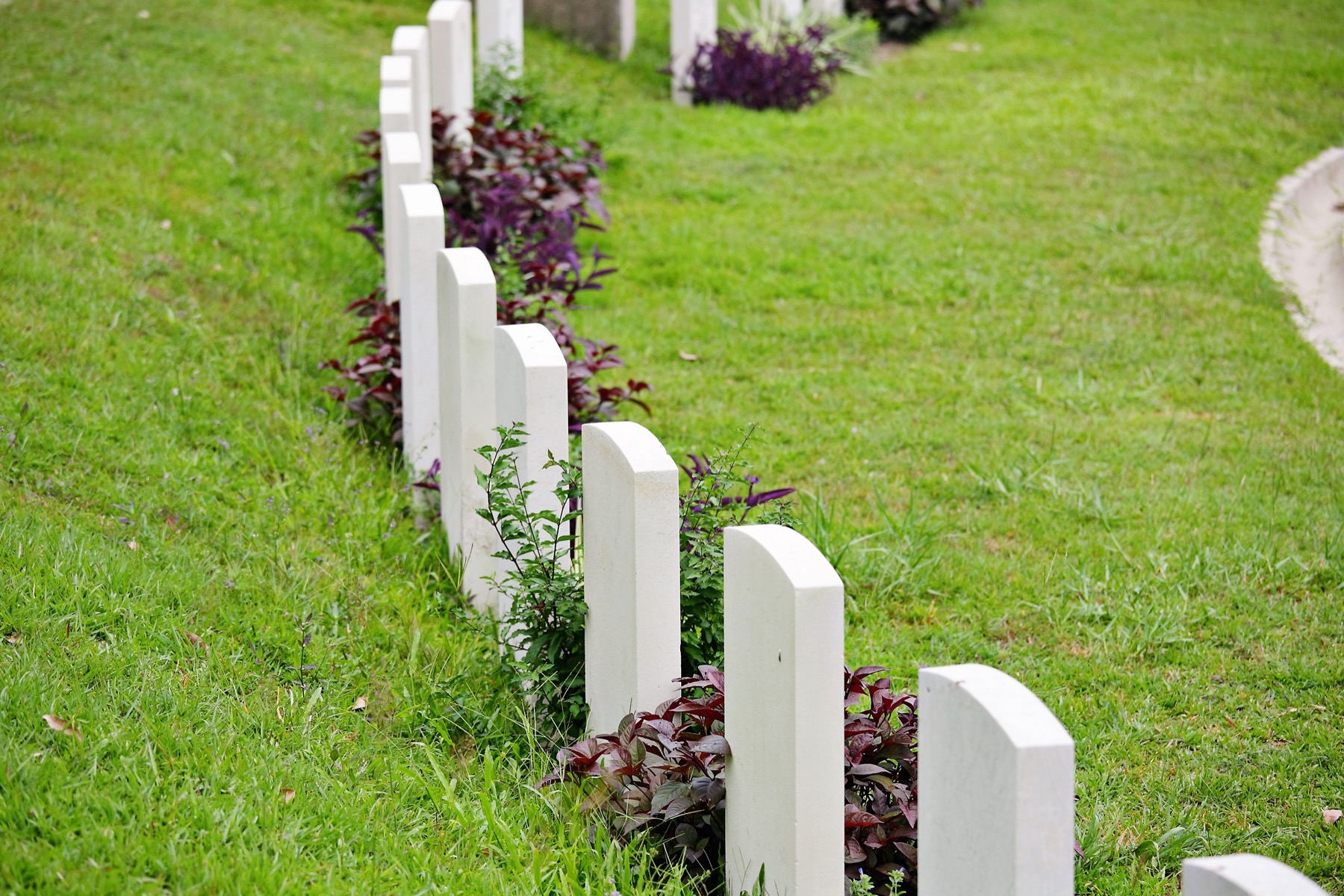

A grave marker, tombstone or head stone is a marker, usually stone, that is placed over a burial plot. They are traditional for burials in the Christian, Jewish and Muslim religions.
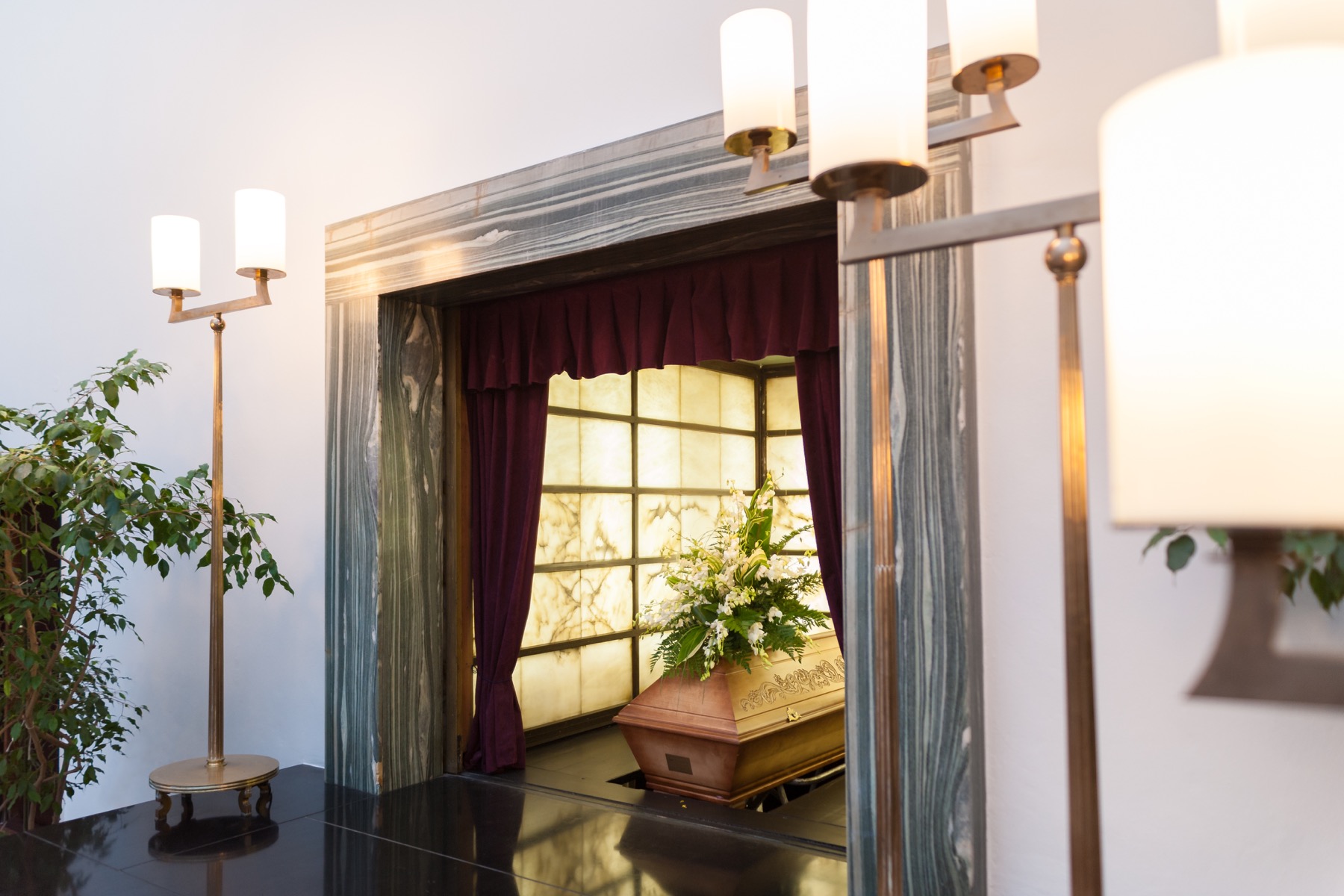

The funeral home as we know it today emerged after the Civil War when the process of embalming came into general practice. Funeral homes were known during the late 18th – 19th century as ‘funeral parlors.’
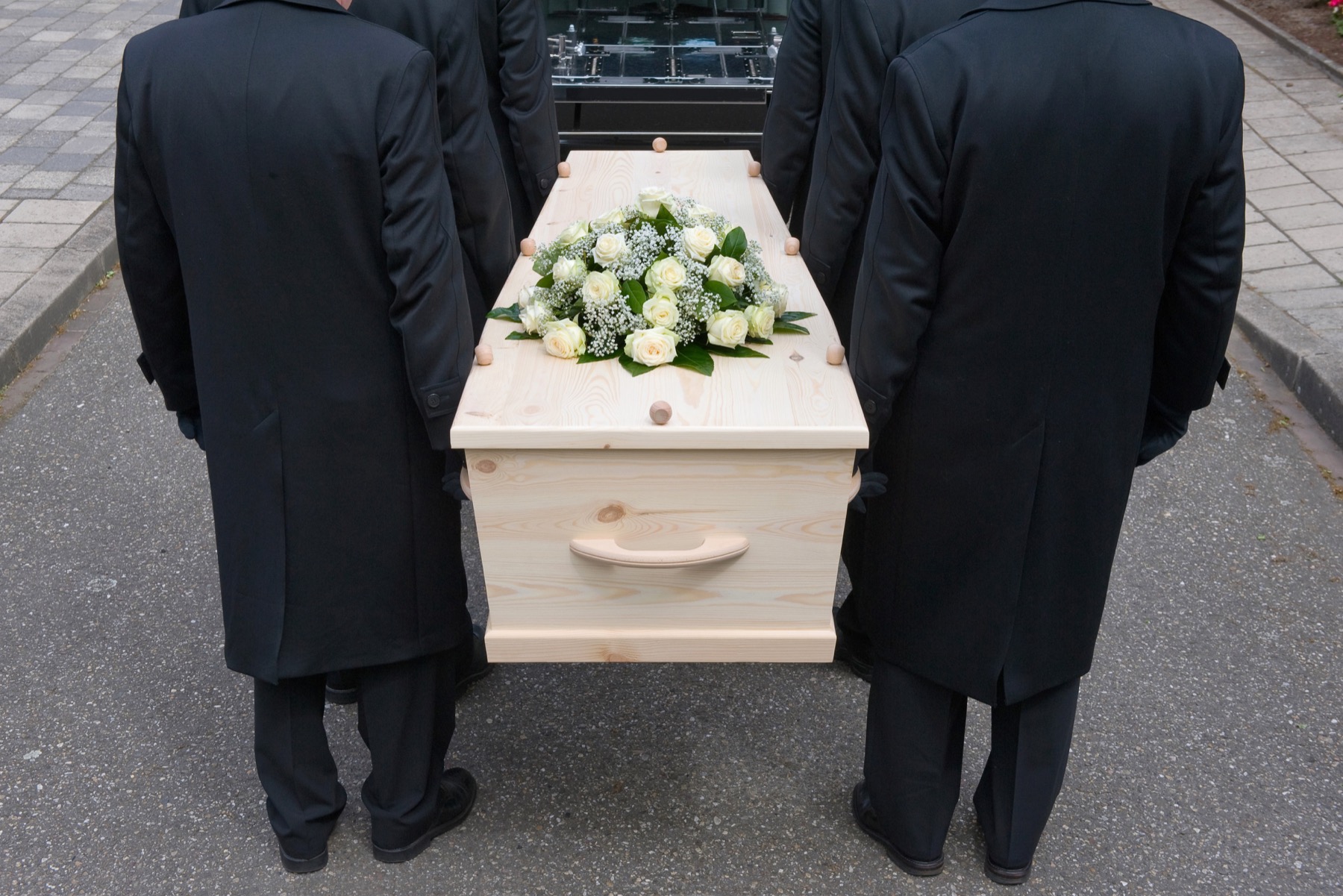

Embracing a new ethic for a new era is driving green burials in the death care industry. A green burial, also called a natural burial is environmentally friendly.
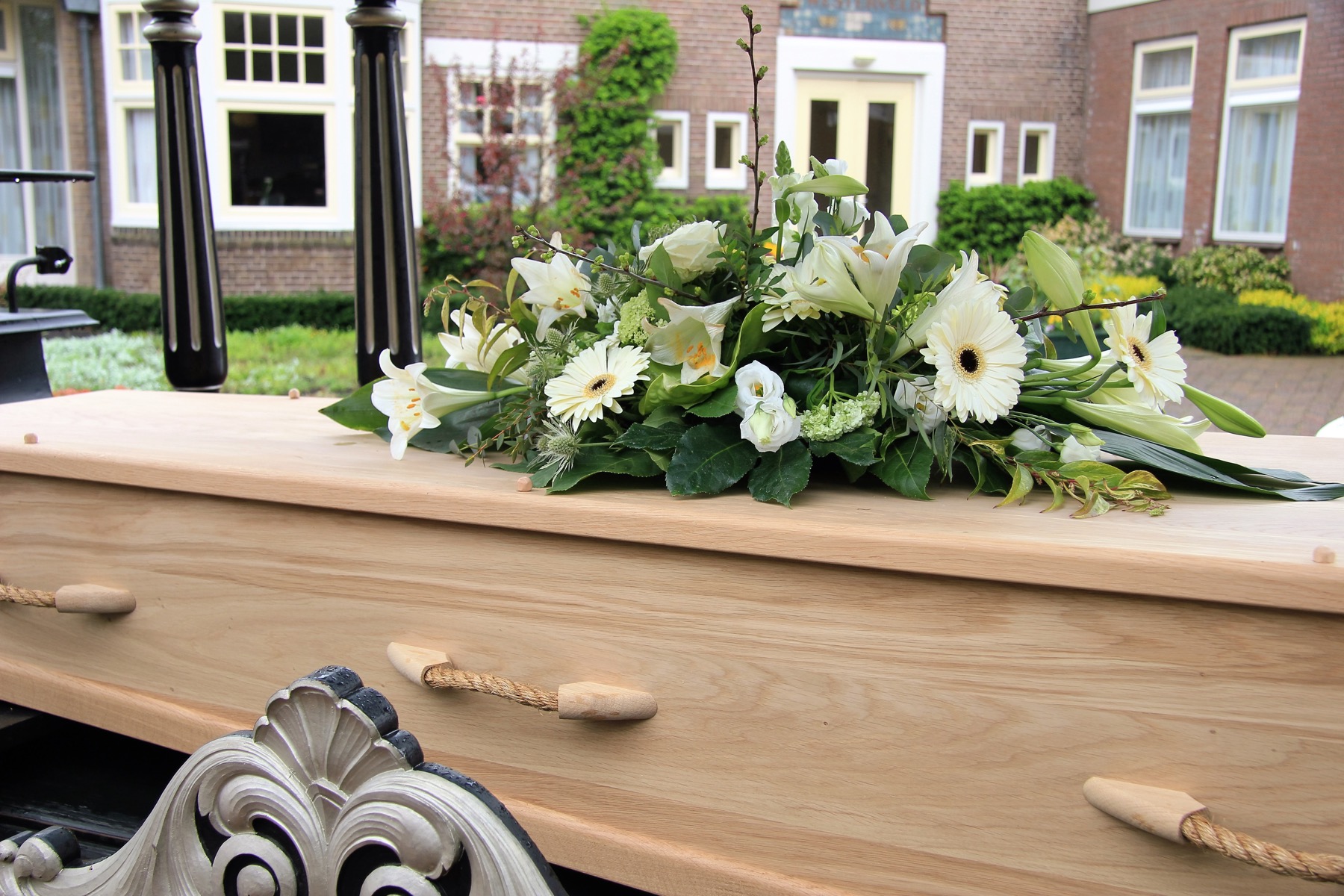

A rental casket has a removable interior. The deceased is placed in a wooden box and the box is placed inside the casket. The body never touches the casket and the wooden box is easily removed.
About JL Memorial
JL MEMORIAL offers a variety of green burial/cremation options, and innovative ways to keep your loved ones memories close.
Contact Us
Subscribe to our Newsletter
We accept all major credit cards

Copyright © 2015-2024 | JL Memorial | All rights reserved
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Supported By WordPress.org